Intraparenchymal hemorrhage
Low confidence
High confidence
- Age: 85
- Sex: Male
- Modality: CT
- Region: Brain
- Country: N/A
- State: N/A
- City: N/A
- Diagnosis: Intraparenchymal hemorrhage
🧠 AI Suggestion
1) Findings:
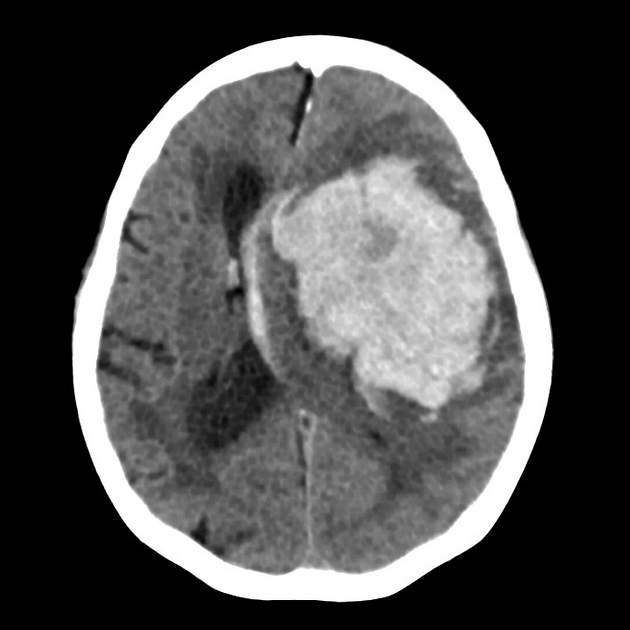
- Large hyperdense intra-axial hematoma centered in the basal ganglia region on the image-right (patient-left).
- Dimensions appear to exceed 4 cm in maximal diameter, consistent with a high-volume hemorrhage.
- Marked surrounding low-density area representing vasogenic edema.
- Significant mass effect with compression of the ipsilateral lateral ventricle and effacement of cortical sulci.
- Midline shift of approximately 8–10 mm towards the image-left (patient-right).
- Deformation and partial effacement of the third ventricle, raising concern for obstructive hydrocephalus.
- No extra-axial hemorrhage evident in this slice.
2) Most likely diagnosis and why:
The most likely diagnosis is a large acute intracerebral hemorrhage involving the image-right (patient-left) basal ganglia. This is supported by the hyperdense appearance of acute blood, classic deep location, and associated edema with mass effect. Hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage is the most common etiology, especially in the basal ganglia region. The degree of shift and ventricular compression indicates a life-threatening presentation.
3) Next best diagnostic step:
The next best step would be urgent CT angiography of the head to exclude an underlying vascular lesion such as arteriovenous malformation, aneurysm, or active contrast extravasation (“spot sign”) that predicts hematoma expansion. CTA is especially important if the patient lacks a history of hypertension, is younger, or if the bleed location is atypical. In parallel, serial CT scans are often performed within 6–24 hours to assess for hematoma growth.
4) Key differential or confirmatory test:
Differential considerations include hemorrhagic transformation of an ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic tumor, but these are best clarified with MRI of the brain (particularly susceptibility-weighted imaging and contrast-enhanced sequences). MRI can reveal underlying neoplasm, cavernoma, or venous infarct. Additional confirmatory evaluation would involve digital subtraction angiography if CTA/MRA raises concern for vascular malformation.
5) Possible treatment or management:
Management depends on hematoma size, neurological status, and mass effect. Emergency neurosurgical evaluation for possible hematoma evacuation (open craniotomy or minimally invasive aspiration) is indicated given large volume and midline shift. Blood pressure control, reversal of coagulopathy if applicable, and intensive monitoring are essential. Ventricular drainage may be needed for hydrocephalus relief. Prognosis is strongly influenced by hematoma volume (>30 mL), GCS on admission, and intraventricular extension
- Large hyperdense intra-axial hematoma centered in the basal ganglia region on the image-right (patient-left).
- Dimensions appear to exceed 4 cm in maximal diameter, consistent with a high-volume hemorrhage.
- Marked surrounding low-density area representing vasogenic edema.
- Significant mass effect with compression of the ipsilateral lateral ventricle and effacement of cortical sulci.
- Midline shift of approximately 8–10 mm towards the image-left (patient-right).
- Deformation and partial effacement of the third ventricle, raising concern for obstructive hydrocephalus.
- No extra-axial hemorrhage evident in this slice.
2) Most likely diagnosis and why:
The most likely diagnosis is a large acute intracerebral hemorrhage involving the image-right (patient-left) basal ganglia. This is supported by the hyperdense appearance of acute blood, classic deep location, and associated edema with mass effect. Hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage is the most common etiology, especially in the basal ganglia region. The degree of shift and ventricular compression indicates a life-threatening presentation.
3) Next best diagnostic step:
The next best step would be urgent CT angiography of the head to exclude an underlying vascular lesion such as arteriovenous malformation, aneurysm, or active contrast extravasation (“spot sign”) that predicts hematoma expansion. CTA is especially important if the patient lacks a history of hypertension, is younger, or if the bleed location is atypical. In parallel, serial CT scans are often performed within 6–24 hours to assess for hematoma growth.
4) Key differential or confirmatory test:
Differential considerations include hemorrhagic transformation of an ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic tumor, but these are best clarified with MRI of the brain (particularly susceptibility-weighted imaging and contrast-enhanced sequences). MRI can reveal underlying neoplasm, cavernoma, or venous infarct. Additional confirmatory evaluation would involve digital subtraction angiography if CTA/MRA raises concern for vascular malformation.
5) Possible treatment or management:
Management depends on hematoma size, neurological status, and mass effect. Emergency neurosurgical evaluation for possible hematoma evacuation (open craniotomy or minimally invasive aspiration) is indicated given large volume and midline shift. Blood pressure control, reversal of coagulopathy if applicable, and intensive monitoring are essential. Ventricular drainage may be needed for hydrocephalus relief. Prognosis is strongly influenced by hematoma volume (>30 mL), GCS on admission, and intraventricular extension
📑 Guidelines Summary (uploaded diagnosis) — Intraparenchymal hemorrhage
Imaging of suspected aneurysm, vascular malformation, or subarachnoid hemorrhage requires tailored modality selection based on presentation and clinical urgency.
- Acute sudden severe headache: non-contrast CT head first-line within 6 hours of onset.
- Negative initial CT but high suspicion: lumbar puncture or CTA can follow.
- CTA head/neck indicated to detect aneurysm, arteriovenous malformation, or vascular stenosis after hemorrhage confirmation.
- MRA head/neck useful in stable patients or when CTA contraindicated.
- Digital subtraction angiography reserved for treatment planning or resolving equivocal CTA/MRA findings.
- No imaging indicated in chronic, stable, nonspecific headaches without red flags or neurologic deficit.
- Red flag triggers include thunderclap headache, focal deficits, papilledema, or rapidly worsening symptoms.
- Time-critical imaging essential for aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage to guide early intervention and reduce rebleeding risk.
- Follow-up vascular imaging recommended after aneurysm repair or AVM treatment to assess recurrence or residual lesion.
- Pitfall: small aneurysms or sentinel bleeds may be missed on early or low-quality CT scans.
- Cerebrovascular Diseases-Aneurysm, Vascular Malformation, and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
- Imaging of Suspected Intracranial Hypotension
🤖 Guidelines Summary (AI diagnosis) — Cerebrovascular Diseases-Aneurysm, Vascular Malformation, and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Guidelines Summary of AI Suggestion diagnosis is the same as the uploaded diagnosis. Please read above.
Comments
No comments yet.
Please log in to comment